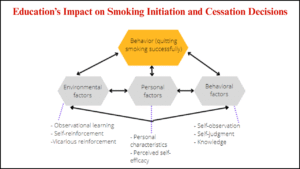
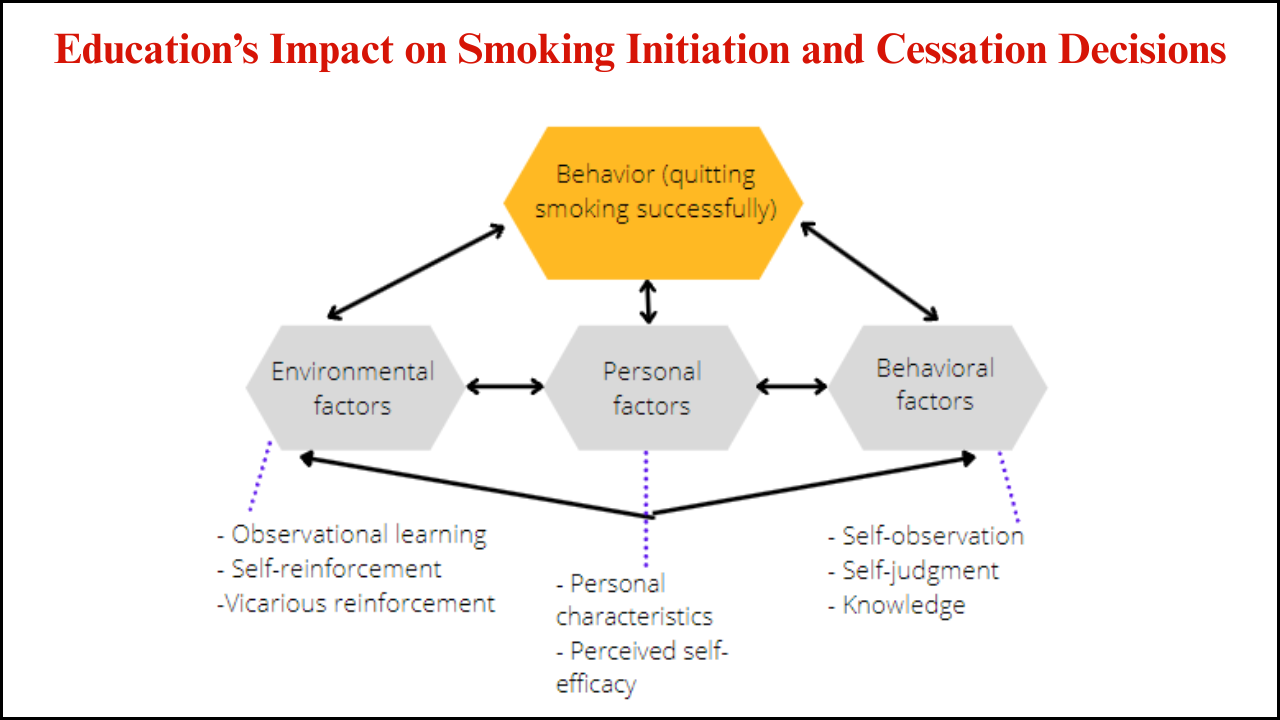
Tobacco control remains one of the most pressing public health challenges globally, and the introduction of Tobacco 21 (T21) laws has been a transformative step toward reducing tobacco-related harm. T21 refers to raising the minimum legal age to purchase tobacco products from 18 to 21 years. Strong enforcement of T21 has been associated with shifts in youth smoking behavior, reductions in maternal smoking during pregnancy, and broader improvements in family health. Examination of youth and maternal health outcomes reveals the far-reaching impacts of T21 enforcement beyond tobacco use reduction.
Table of Contents
Key Features of T21 Enforcement
- Age Restriction: Retailers are prohibited from selling tobacco products to anyone under the age of 21.
- Retailer Compliance Checks: Governments and public health agencies conduct frequent inspections to ensure adherence.
- Penalties for Violations: Non-compliant retailers face fines, license suspensions, or revocations.
- Community Engagement: Awareness campaigns educate both youth and parents about the risks of tobacco.
- Policy Integration: T21 laws are often combined with smoke-free policies, taxation, and cessation support.
Effects on Youth Health Outcomes
Youth smoking behaviors show the most immediate changes after T21 enforcement.
- Reduced Initiation of Tobacco Use
- Most smokers begin before age 21; raising the legal age interrupts this pattern.
- Adolescents find it harder to access tobacco through peers who are legally allowed to purchase.
- Lower Risk of Nicotine Addiction
- Brain development continues until the mid-20s, making youth more susceptible to addiction.
- T21 reduces exposure during the most vulnerable period.
- Decline in E-Cigarette and Vaping Use
- Vaping products, which were popular among teens, also fall under T21 restrictions.
- Youth report fewer opportunities to purchase vaping devices.
- Improved Academic and Social Outcomes
- Less tobacco use correlates with better concentration in schools.
- Peer pressure to smoke decreases as access becomes restricted.
Youth Health Outcomes after T21 Enforcement
| Outcome | Observed Effect | Public Health Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Smoking initiation | Significant reduction among high school students | Delayed or prevented tobacco use onset |
| Nicotine addiction | Lower prevalence in individuals under 21 | Reduced long-term dependency rates |
| Vaping and e-cigarette use | Decline in sales and self-reported usage | Lower respiratory risks and addiction |
| Peer access to tobacco | Decreased due to older peers being restricted | Reduced social availability |
| Academic performance | Improved focus and attendance | Positive effect on educational outcomes |
Effects on Maternal Health Outcomes
Maternal health is closely linked to tobacco exposure, both active and passive. T21 enforcement influences maternal well-being through direct smoking reduction and environmental changes.
- Reduced Maternal Smoking during Pregnancy
- Young expectant mothers are less likely to smoke due to reduced accessibility.
- This lowers the risks of premature birth, low birth weight, and stillbirth.
- Decreased Secondhand Smoke Exposure
- Families experience cleaner home environments as fewer household members smoke.
- Pregnant women face fewer health complications from secondhand smoke.
- Improved Birth Outcomes
- Studies show lower rates of neonatal intensive care admissions in areas with strong T21 laws.
- Infants have higher average birth weights and healthier developmental starts.
- Strengthened Cessation Efforts
- Pregnant women attempting to quit find more supportive environments when fewer peers smoke.
- Healthcare providers integrate T21 with cessation counseling.
Maternal Health Outcomes after T21 Enforcement
| Maternal Outcome | Observed Effect | Health Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Maternal smoking during pregnancy | Decline among women under 21 | Lower risk of complications and infant mortality |
| Secondhand smoke exposure | Reduction in household exposure | Improved maternal respiratory health |
| Birth weight outcomes | Higher average birth weights | Reduced neonatal complications |
| Preterm births | Fewer cases reported | Stronger early childhood development |
| Maternal cessation support | Enhanced social support for quitting | Long-term maternal health benefits |
Community and Family-Level Impacts
- Improved Household Health: Fewer smoking adults in households reduces exposure for children and pregnant women.
- Positive Generational Effects: Mothers who avoid smoking during pregnancy are less likely to raise children who smoke.
- Health Equity Improvements: T21 enforcement reduces disparities, especially in low-income communities where tobacco use is higher.
- Economic Benefits: Families save money on healthcare costs related to tobacco-related illnesses.
Public Health and Policy Outcomes
- Stronger Preventive Health Systems
- T21 supports long-term health planning by lowering future burdens of tobacco-related disease.
- Healthcare Savings
- Fewer premature births and chronic diseases reduce medical expenditures.
- Increased Awareness
- Public education campaigns tied to T21 enforcement boost awareness about maternal and youth risks.
- Cultural Shifts
- Smoking becomes less socially acceptable, further reinforcing preventive efforts.
Broader Public Health Implications of T21
| Area of Impact | Change After T21 Enforcement | Long-Term Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Preventive healthcare | Stronger focus on youth and maternal health | Reduced healthcare burden |
| Economic outcomes | Lower medical costs for families and states | Improved financial security |
| Public awareness | Higher understanding of tobacco risks | Sustained cultural change |
| Health equity | Narrowed gaps between income groups | Fairer health outcomes |
| Chronic disease prevention | Lower rates of cancer, heart disease | Increased life expectancy |
Challenges in T21 Enforcement
- Retailer Compliance Issues
- Some stores still sell to underage individuals, especially in areas with weak oversight.
- Social Access Routes
- Youth may obtain tobacco from family members or through online purchases.
- Need for Education
- Awareness campaigns are necessary to inform communities about the law.
- Variation in Enforcement
- Outcomes differ depending on how strictly local governments enforce T21.
Future Directions
- Integration with Maternal Health Programs: Combining T21 with prenatal care and cessation support.
- Stronger Online Sales Regulation: Preventing youth access through digital platforms.
- Expanded Research: Longitudinal studies tracking outcomes across multiple generations.
- Community Engagement Models: Involving schools, parents, and healthcare workers in enforcement.
Closing Reflections
T21 enforcement plays a critical role in shaping healthier futures for youth and mothers. Evidence shows that raising the minimum tobacco purchasing age reduces smoking initiation, lowers nicotine addiction, and supports healthier pregnancies. Community health benefits expand beyond individuals to households and society, creating ripple effects of prevention. Strong enforcement, combined with education and support systems, ensures that T21 laws reach their full potential in protecting future generations.